IJERPH - mega journal
The International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health has grown rapidly in recent years. It now publishes so many papers it is classed a mega journal. Concerns have been raised about MDPI, IJERPH’s publisher, with debate about whether it is a predatory publisher or not or something in-between.
Impact trouble
Recently, Clarivate delisted IJERPH so it no longer has an “official” impact factor. This is a big blow as researchers are often judged on the impact factor of the journal they publish in. So the higher the impact factor the better. For a mega journal in public health, IJERPH’s impact factor was impressive, although there is evidence that this was due to impact factor inflation.
Nothing special
Publishing papers in special issues seems key to MDPI’s and IJERPH’s growth. There is really nothing special about special issues in IJERPH as the majority of IJERPH’s papers in 2022 were in special issues. One aspect yet (I think) to be explored is the use of special issues to self publish. A special issue is edited by the people who proposed its topic rather than the normal editors (although they may have input). It is not uncommon for IJERPH editors to also author a paper in a special issue.
Self publishing
Obviously it is well recognised that if an editor is an author on a submitted paper to their journal (or special issue) then the editor should not be involved in decisions relating to that paper. MDPI’s guidelines are as follows:
Editor’s Submission: The special issue may publish contributions from the Guest Editor(s), but the number of such contributions should be limited, to ensure the diversity and inclusiveness of authorship representing the research area of the Special Issue. Any article submitted by a Guest Editor will be handled by a member of the Editorial Board.
I calculated that a fifth (20.1%) of all papers (excluding editorials, comments, erratum and retractions) in special issues in IJEPHR have an editor as an author, with just under three quarters (73.5%) of special issues having at least one paper with an editor as an author. My calculations are based on analysis of all papers (11059) published in special issues (1271) that closed for submissions from the start of 2022 to the end of March 2023. I was able to link authors and editors in special issues through their Sciprofile profile (an author network site run by MDPI on which each author and editor seems to have their own page).
How fast?
MDPI facilitates quick peer review. Prof Dorothy Bishop explored Editor Response Time (RT) for some Hindawi’s journals. She found that special issue papers were reviewed much faster. This inspired me to look at IJERPH and I found review times for 2022 for special issues and non special issue papers for this journal were similar (and similar to a Hindawi journal’s special issue). I extend the analysis here - using my data from special issues that closed for submissions 2022/March 2023- to compare special papers where the editor is an author to where they are not. The average time from paper receipt to paper revision was 37.7 days for papers where an editor was not an author and 36.9 days for where an editor was an author. That’s a difference of -0.86(95% CI, -1.69 to -0.03). Comparing within special issues (i.e each paper to the mean of that special issue) - to account for differences between special issues - revealed that editor authored papers continued to have a lower turn around time -1.61(95% CI, -2.51 to -0.7). Figure 1 shows the distribution of times.
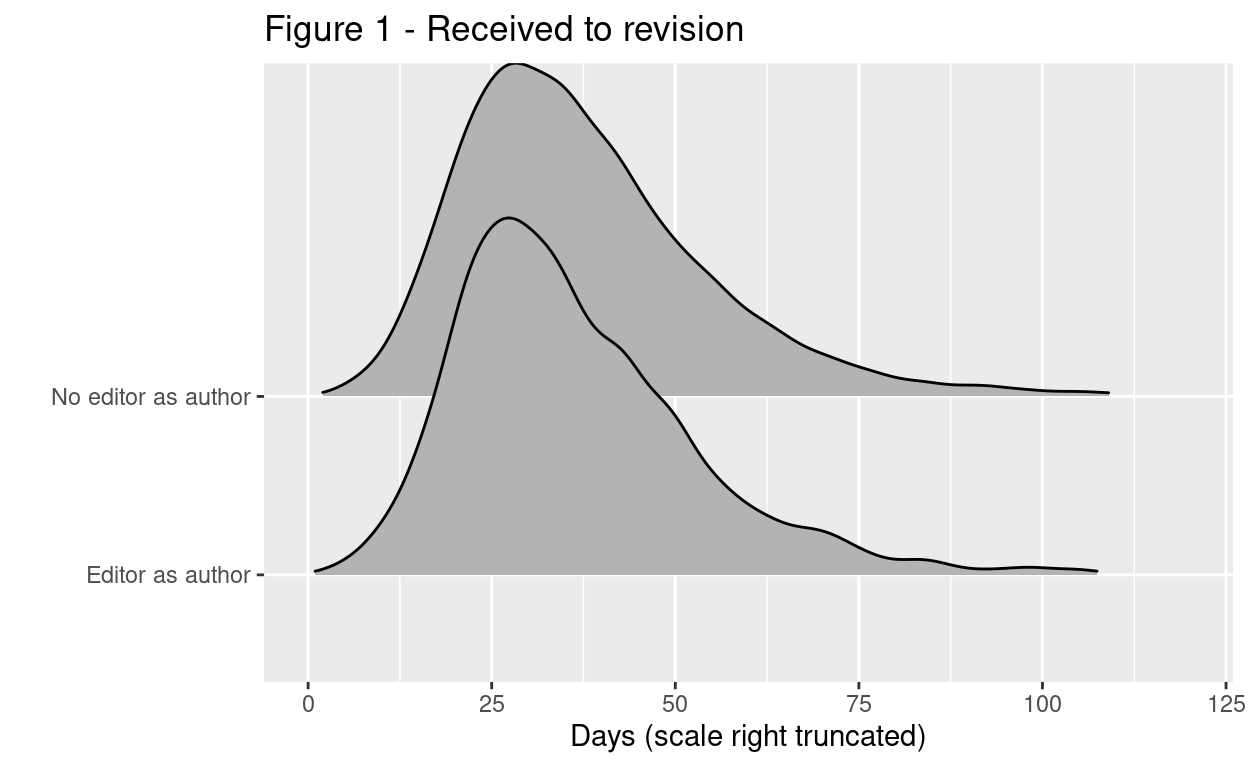
Summary
The majority of special issues feature editor authored papers. If anything the review process is speedier for such papers. What does this mean? I don’t know really. Personally I am surprised at the level of self publishing and its speed (I would have thought that having to involve an usual editor would delay the process). My analysis may contain mistakes so you can view the analysis code and the code used to construct the datasets as well as the datasets (1 and 2).
Thanks
R, RStudio, tidyverse, broom, broom.mixed, distill, panelr, ggridges, glue rvest rentrez RefManageR rcrossref